Which types of penetration testing are suitable for your business?
Ensuring the security of systems and networks is very important in today’s digital world. One of the most effective ways to assess vulnerabilities and reinforce security measures is through penetration testing. There are different types of penetration testing available, each serving a specific purpose depending on the level of access testers have. So which types of penetration testing should you choose?
Types of penetration testing – Black Box Penetration Testing
Definition
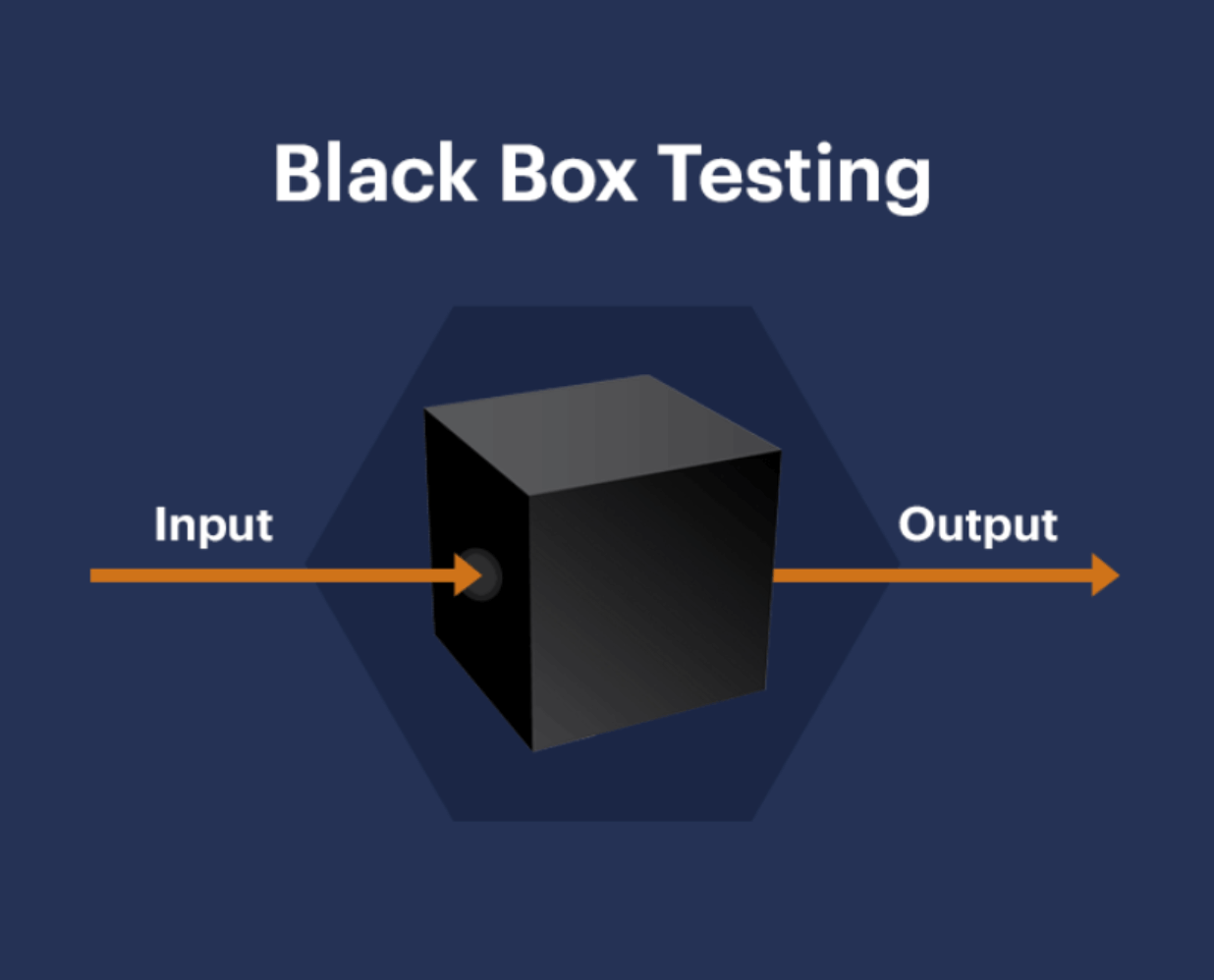
Black Box Penetration Testing is one of the common types of penetration testing, where the tester has no information about the system or application they are attacking. Similar to a real hacker, they must find a way to penetrate the system from the outside without being provided with internal information such as source code, system architecture, or access to security documents. This method simulates a real external attack on the system, allowing the identification of vulnerabilities that an attacker could exploit to infiltrate the system without needing to understand how the system operates internally.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
|---|---|
When to Use It?
Black Box Penetration Testing is commonly used when an organization wants to assess the security level of a system from the perspective of an external attacker. Among the different types of penetration testing, this method is ideal when the goal is to test publicly accessible web applications, network systems, or online services.
Read Effective Tools in Penetration Testing to Ensure Network Security
For example, if you are deploying a new web application and want to ensure it can withstand external attacks, Black Box Testing would be a reasonable choice. This method will help you discover weaknesses in the system that may not have been exposed during the development process.
White Box Penetration Testing
Definition
White Box Penetration Testing, also known as white-box testing, is a security testing method where the tester has full access to all internal information of the system, including source code, system architecture, network diagrams, and other security-related documents. The goal of this method is to evaluate the security from within, identifying potential security vulnerabilities that external testing methods may not detect.
In White Box Testing, the tester uses the internal information to carry out simulated attacks in order to assess the system’s security. This allows them to examine the complex internal elements of the system, ensuring that no security vulnerabilities are overlooked, making it one of the most thorough types of penetration testing.

Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
|---|---|
|
– Comprehensive testing: White Box Penetration Testing allows for a detailed examination of the entire system from within, helping to identify vulnerabilities that other testing methods can’t detect. – High efficiency: Since the tester has access to the source code and related documents, the identification and remediation of security vulnerabilities become faster and more accurate. |
– Dependent on code quality: If the system’s code has been well-written and adheres to security principles, White Box Testing may not reveal many new vulnerabilities. – Requires high-level skills: White Box Testing demands deep expertise in source code analysis and system design, making the process challenging for those without sufficient expertise. |
When to Use It?
White Box Penetration Testing is one of the types of penetration testing that is suitable for organizations that have developed complex internal systems and want to ensure that all internal elements are secure. This method is particularly useful when you need to test critical internal applications such as financial systems, data management systems, or services requiring high security.
Read How independent testing improves software reliability and reduces risks?
White Box Penetration Testing helps organizations evaluate the security of internal elements such as data encryption, access control, and user account management. This method provides deep insights into the system’s security through internal analysis, allowing organizations to identify and remediate vulnerabilities effectively.