Types of project management methods for business
Project management is pivotal in guiding projects from conception to completion, ensuring they meet objectives while staying within time and budget constraints. Understanding the different types of project management methods is crucial for choosing the right approach tailored to specific project needs. This article explores various project management methodologies that can enhance efficiency and effectiveness in business projects.
Understanding project management
Definition and objectives of project management
Project management is the discipline of planning, organizing, and managing resources to bring about the successful completion of specific project goals and objectives. The primary objectives of the types of project management include the completion of projects on time, within budget, and in scope, while meeting or exceeding stakeholders’ expectations.
Core components of project management
The core components of the types of project management include scope, resources, time, and budget management. Each component plays a critical role in the success of a project:
- Scope management: Defines and controls what to include and exclude in the project.
- Resource management: Ensures that necessary resources (people, equipment, material) are available to execute the project.
- Time management: Involves planning the timeline for the project and ensuring tasks are completed as scheduled.
- Budget management: Oversees the financial constraints of the project, ensuring allocated budget.

Types of project management traditional methods
Waterfall method
The Waterfall method is a straightforward project management technique where tasks are completed in a sequential order. The “Waterfall” name comes from the method’s characteristics – each phase cascades into the next, like water flowing over a series of steps. It follows a highly structured and linear process, meaning each stage of a project must be completed before the next one begins, with no overlap.
The Waterfall method is best suited for projects with clear, fixed requirements that are unlikely to change. It works well when the technology is well understood and the project’s scope is clear from the outset. Here are some typical scenarios where this types of project management is effective:
- Construction projects: Where blueprints, which are analogous to project plans, are created early in the project, and changes later in the project can be very costly.
- Software Development: Particularly in industries like aerospace or pharmaceuticals, where changes can be extremely risky and require rigorous testing and compliance with regulations.
Critical path method (CPM)
Another popular method is the Critical Path Method (CPM), it helps project managers plan and schedule complex projects. By focusing on critical tasks and timelines, CPM aims to complete projects in the shortest time possible.
CPM is ideal for projects with numerous activities and dependencies where delays can be costly. This types of project management is particularly useful in complex projects, such as:
- Construction projects: Large-scale building projects with sequential and interconnected tasks.
- Engineering projects: Projects that involve detailed steps that must occur in a specific order to achieve technical requirements.
- Event planning: Large events where delays in certain preparations could jeopardize the event’s timing.
Types of project management popular methods
Agile methodology
Scrum framework
The Scrum framework is a popular agile project management methodology. It’s used primarily in software development but is increasingly adopted by other fields due to its flexibility and effectiveness. Scrum helps teams work together by breaking down large projects into small, manageable pieces. These pieces can be completed incrementally.
The Scrum relies heavily on teamwork, accountability, and iterative progress towards a well-defined goal. It’s structured around a series of sprints, which are fixed-length periods (usually 2 – 4 weeks), where specific work has to be completed and made ready for review.
Scrum is particularly effective in projects that are complex and where requirements are subject to change frequently. This makes it suitable for software development, product development, and other fields that require a high level of innovation and flexibility.

Lean project management
Lean project management is a methodology that aims to deliver maximum value while minimizing waste. It’s derived from lean manufacturing practices pioneered by Toyota in the automotive industry and has since been adapted across various sectors, including construction, software development, and healthcare. The core principle of lean is to streamline operations, reduce waste, and improve overall efficiency, leading to better outcomes and customer satisfaction.
Lean project docates for types of project management that are particularly effective in environments where there is potential to streamline operations and reduce waste. It’s suitable for:
- Manufacturing: Where reducing material waste and improving production times are crucial.
- Software development: Where there is a need to deliver features that meet user needs quickly and efficiently.
- Healthcare: Where improving patient flow and service quality is critical.
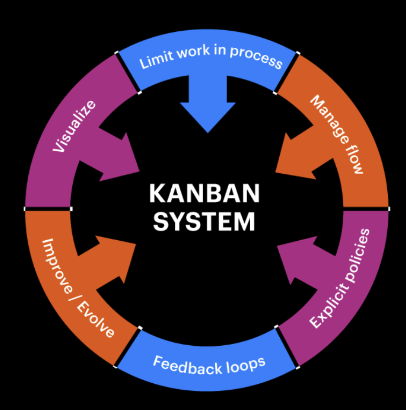
Kanban method
The Kanban method is a popular type of project management technique that emphasizes continuous collaboration and efficiency. The suitable type of environment for this method is where the team continuously works and frequently changes the scope. Kanban helps teams manage the flow of tasks as they move through different stages of the process.
Kanban’s best used where projects require continuous output, like in manufacturing or ongoing software maintenance. It’s especially effective in environments that require robust workflow visualization. Kanba will be a popular choice in the following contexts:
- Software development and IT services: require flexibility to handle tasks that vary in nature and priority. This flexibility is essential to accommodate changing client needs.
- Marketing teams: where different types of tasks, such as campaigns, creative production, and event planning, need to be managed simultaneously.
- Operational processes: In settings like hospitals or repair services, where different tasks need quick attention and prioritization.
Six sigma
Six Sigma is a data-driven approach which used to improve the quality and efficiency of operational processes. This methodology aims to reduce variability and defects in everything from manufacturing to service delivery, ensuring products and services meet high-quality standards consistently.
This method is effective in projects that aim for near perfection in quality. Six Sigma is commonly applied in industries where mistakes can lead to significant financial losses or safety concerns. Typical scenarios include:
- Manufacturing: Reducing scrap rates and warranty costs.
- Healthcare: Reducing errors in patient care and administrative processes.
- Financial services: Minimizing errors in billing and transaction processes.
How to choose the right project management methodologies?
Choosing the right types of project management methodology is a crucial decision that can impact the success of a project. Various methodologies offer different frameworks, processes, and guidelines that can significantly influence project execution and outcomes. Here’s a simple and clear guide on how to select the right types of project management methodology based on key factors.
Consider project scope
The scope of a project defines what needs to be accomplished. A clear understanding of the project scope helps determine how flexible or strict the management approach needs to be:
- Fixed scope: Projects with fixed and clear deliverables, such as constructing a building or developing a standard software package, often benefit from traditional types of project management like the Waterfall method. This is because these projects have well-defined stages and requirements that are unlikely to change once the project begins.
- Flexible scope: Agile methodologies (like Scrum or Kanban) are better suited for experimental projects or those likely to undergo changes, such as software development in a rapidly changing market. These methods allow for flexibility and regular revisions to the project scope based on ongoing feedback and evolving requirements.

Assess industry requirements
Different industries have different regulatory, quality, and safety standards that can influence the choice of types of project management methodology:
- Regulated industries: In industries such as pharmaceuticals, aerospace, and construction, where companies must comply with strict regulatory standards, methodologies that emphasize thorough documentation and strict milestone reviews (e.g., Waterfall) are preferable.
- Creative and dynamic industries: In sectors like marketing, software, or product design, where companies prioritize innovation and speed, agile methodologies that support creativity and rapid iteration, such as Agile or Lean, are more effective.
Evaluate team size
The team size and how it s distributed can also impact the choice of types of project management:
- Small teams: Smaller teams often benefit from more flexible and less formal structures, such as Scrum or Kanban, which allow for quick communication and faster decision-making.
- Large teams: Large projects involving many team members, possibly distributed across different locations, might require more structured methodologies like Waterfall or Six Sigma, which help in coordinating efforts and maintaining discipline through formal procedures and documentation.
Consider project complexity
The complexity of a project can vary widely from simple tasks to complex integrations:
- High complexity: Projects with high complexity, multiple dependencies, and critical paths benefit from using methodologies like the Critical Path Method (CPM) or Six Sigma, which focus on meticulous planning and precision.
- Moderate to low complexity: Projects with fewer complexities are well-suited to leaner methods such as Agile or Lean project management, which focus on eliminating unnecessary work and improving efficiency.
Match methodology to project lifecycle
Consider how different methodologies align with the project lifecycle:
- Short-term projects: Short, fast-paced projects may require methodologies that allow for rapid execution and flexibility, such as Agile methods.
- Long-term projects: Phased approach ass Waterfall method would be more suitable for projects with a longer timeline and fixed requirements.
Selecting the right types of project management methodology is more than just a procedural decision. It can significantly impact its success or failure. By understanding the strengths and limitations of each methodology, businesses can better match their project needs with the appropriate management style, leading to enhanced project outcomes and business success.








